There are many definitions over
employee engagement and according to Macleod, (2018) Employee engagement is a
workplace approach resulting in the right conditions for all members of an
organization to give of their best each day, committed to their organization’s
goals and values, motivated to contribute to organizational success, with an
enhanced sense of their own well-being.
According to Armstrong, (2014) employee engagement is the “Engagement
takes place when people are committed to their work and the organization and
are motivated to achieve high levels of performance".
Employee Engagement Model
Figure i: IES model
of employee engagement: Armstrong, (2014)
Source: Armstrong's
handbook of human resource management practice.
As another references Hewitt, (2012)
introducing The Aon Hewitt Engagement Model of employee engagement as show as
below and further he explains through this model observes engagement outcomes
as Say, Stay, and Strive.
- Say - speak positively about the organization to coworkers, potential employees, and customers
- Stay - have an intense sense of belonging and desire to be a part of the organization
- Strive - are motivated and exert effort toward success in their jobs and for the company
Figure ii: The Aon
Hewitt Engagement Model: Hewitt, (2012)
Source: 2015 Trends
in Global Employee Engagement
Trends in Global Employee Engagement
Many organizations are thus
measuring employee engagement in regular employee surveys as an important
business indicator. As example it could be mentioned Hewitt, (2012) conducted
research on Global levels of employee engagement continue to trend upward. It
conducted because it is significant the great recession and globally the
engagement has moved up from 61% to 62%.
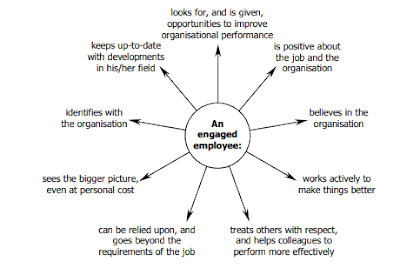
Characteristics of Employee Engagement
Robinson, Perryman and Hayday, (2004)
explain below characteristics of an engaged workforce.
Figure iii: Characteristics of an engaged
employee: Robinson, Perryman and Hayday, (2004)
Source: The Drivers
of Employee Engagement
Employee Satisfaction vs. Employee Engagement
Thought out the research of
Maylett, (2012), identified five key of employee engagement factors, and Regal,
(2018) explain it more clearly using “MAGIC”
concept which is easy to remember. And he
mentioned that “Employee
satisfaction is the minimum entry fee that needs to be met for an employee
to be fully engaged”.
Figure iv: Employee
Satisfaction vs. Employee Engagement in 2018: Rogel, (2018).
Source: https://www.decision-wise.com/job-satisfaction-vs-employee-engagement/
Employee Satisfaction
As Rogel, (2018) describes most
of the managers mistakenly think that
employee satisfaction can increase employee motivation and elaborate American
psychologist Frederick Herzberg's Motivation Hygiene theory proposes
that people are influenced by two factors: those that impact motivation and
basic factors that influence job satisfaction which is called Hygiene factors.
It is being clearly briefed below.
- Hygiene factors- Determine a person’s level of satisfaction with their job. It is strongly influence employee retention and if unable to meet, resulting to job dissatisfaction and cause employees to look for better opportunities from outside.
- Motivation factors- Influence on how person performs the job. If an employee motivated, then invest more in their work and strive to do better for themselves.
Figure v: Job
Satisfaction Won’t Buy You Engagement: Rogel, (2018).
Source: https://www.tlnt.com/job-satisfaction-wont-buy-you-engagement/
Outcomes of engagement
Stairs and Galpin (2010) describe
that following out comes of high levels of engagement,
- Lower absenteeism and higher employee retention
- Increased employee effort and productivity
- Improved quality and reduced error rates
- Increased sales
- Higher profitability, earnings per share and shareholder returns
- Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Faster business growth
References
Armstrong, M. and Taylor, S., (2014). Armstrong's handbook of human resource management
practice. Kogan Page Publishers.
Armstrong, M., (2009). Armstrong’s Handbook Of human
resource Management practice 11th edition.
Charles Rogel, (2018). Employee Satisfaction vs.
Employee Engagement in 2018. [Online]
Available at: https://www.decision-wise.com/job-satisfaction-vs-employee-engagement/
[Accessed 25 9 2018].David Macleod, (2018). What is Employee Engagement. [Online]
Available at: http://engageforsuccess.org/what-is-employee-engagement
[Accessed 25 9 2018].
Frederick, H., (1966).
Work and the Nature of Man. Cleveland:
World Publishing Company.
Hewitt, A., (2012). 2012 Trends in global employee
Engagement. Aon Hewitt Corp,
p.18.
Robinson, D., Perryman, S. and Hayday, S., (2004). The
drivers of employee engagement: Institute of Employment Studies Report
408. United Kingdom, London:
Publisher unknown.
Stairs, M. and Galpin, M., (2010). Positive engagement: From
employee engagement to workplace happiness.
Tracy Maylett, (2012). Engagement
Magic. [Online]
Available at: https://www.decision-wise.com/5-keys-of-employee-engagement-magic/
[Accessed 25 9 2018].




Good in-text citations, referencing and contents are good.
ReplyDeleteArticle accepted.
Described well, good read.
ReplyDeleteWell structured...
ReplyDeleteNicely arranged article with latest references...
ReplyDeleteEmployee engagement is a big concern for every corporate company. SOS brings you the ultimate list of Online employee engagement activities for employees to keep remote workers connected and motivated.
ReplyDelete